TECHNOLOGY
Plasma Antennas
Devices that relies on a plasma discharge to transmit, receive, or reflect electromagnetic waves.
STEALTH
WHEN TURNED OFF
ELECTRICALLY
RECONFIGURABLE
REDUCED
INTERFERENCES
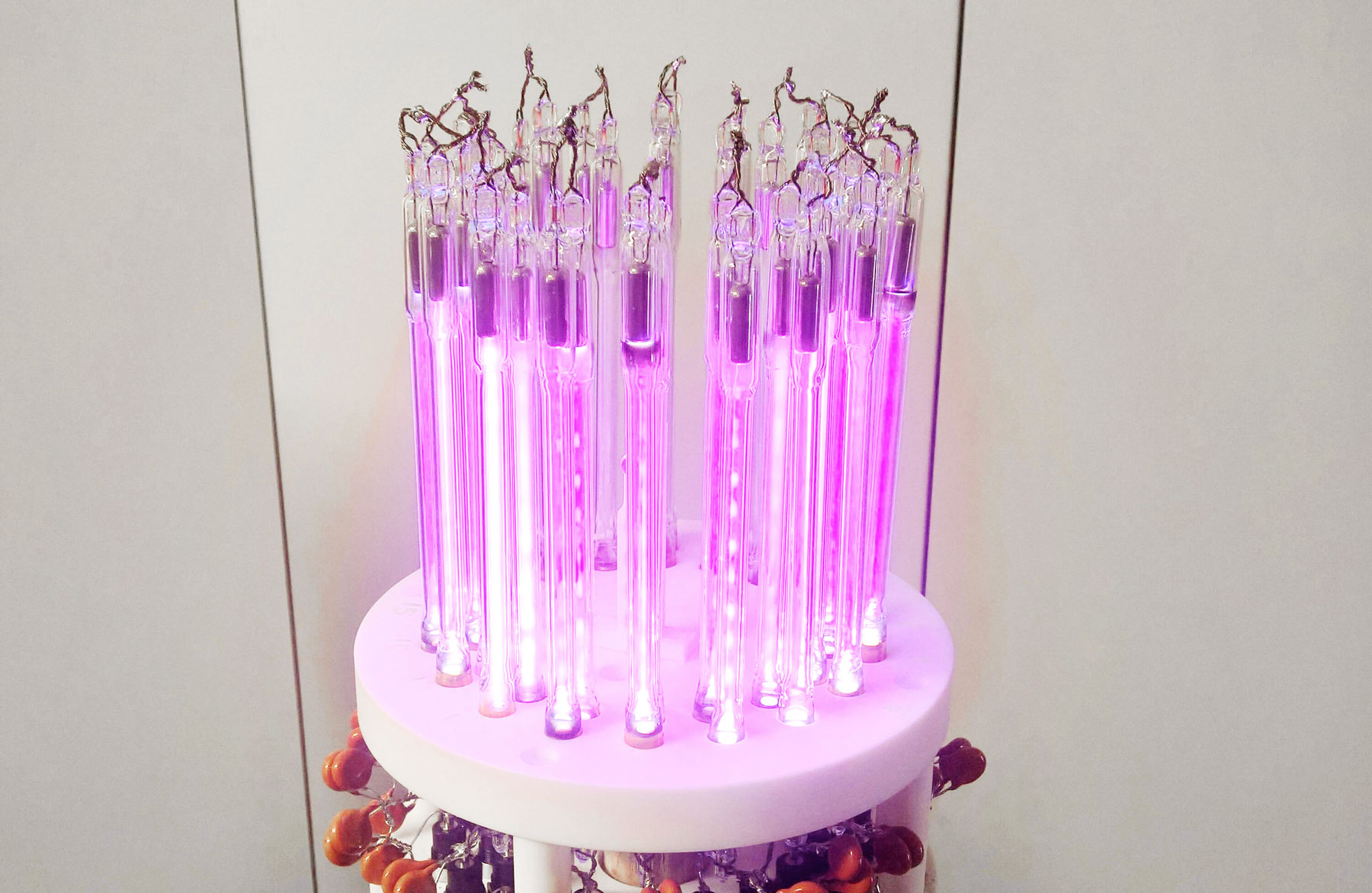
L-BAND REFLECT ARRAY
A metal dipole surrounded by 18 couples of plasma discharges. By turning on and off the discharges, the pattern can be steered and focused towards the desired direction.

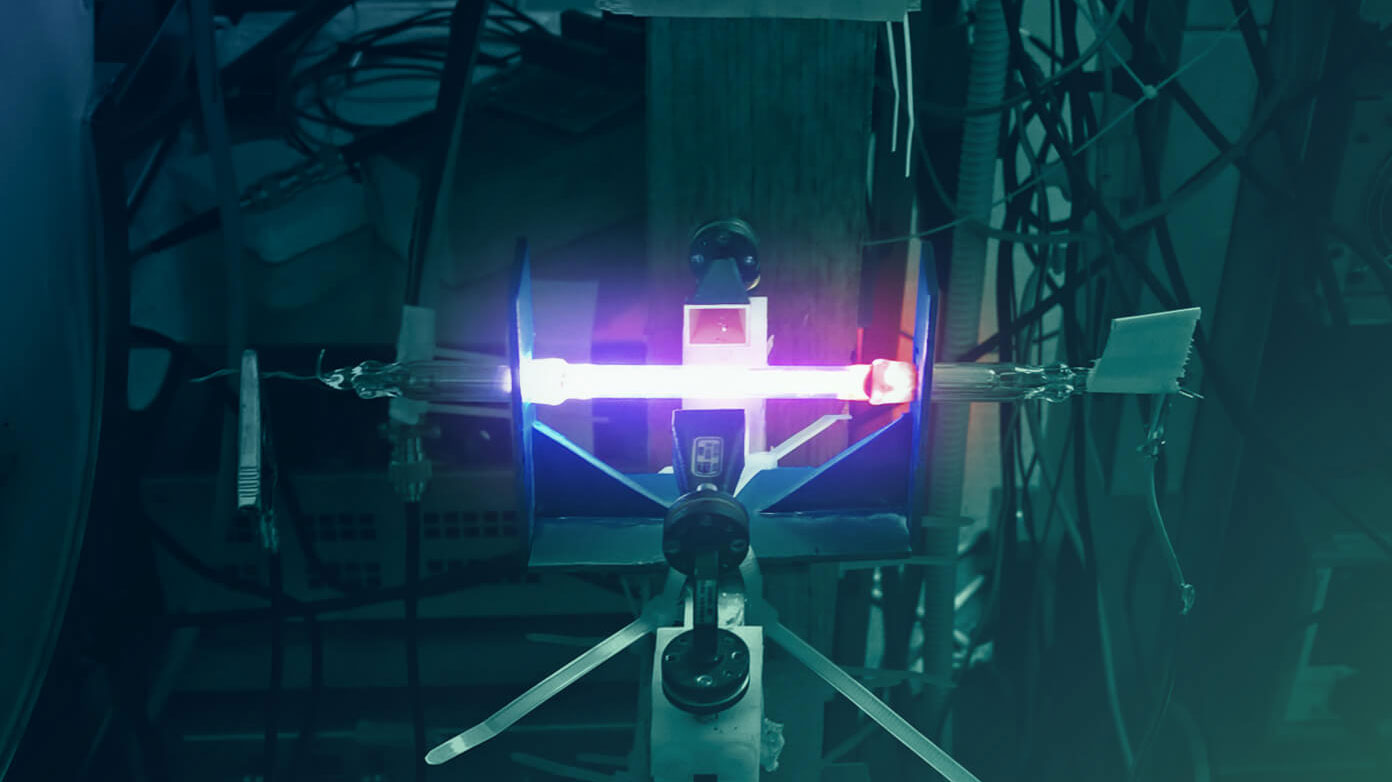
UHF PLASMA DIPOLE
Two plasma discharges placed as the arms of a conventional dipole.
When the plasma is on, it behaves as a conventional dipole. When the plasma is off, the Radar Cross Section is minimized.
TECHNOLOGY
Plasma antenna uses plasma instead of metal to receive, transmit or reflect EM waves.
We design, manufacture and characterize plasma discharges specifically designed to be applied in plasma antennas.
The discharges are closed vessels made of dielectric material (e.g. glass) with one metal electrode at each end, filled with inert gas at low pressure.
When the gas it is energizes, it becomes plasma. Under certain conditions, plasma is a conductive medium and it can be used to transmit or receive EM waves through a circuit call “signal coupler”.
When the antenna is not in use, the power to the plasma can be turned off, and the antenna reverts to a neutral gas enclosed in a dielectric vessel with few metal parts. In this conditions, the Radar Cross Section of the plasma antenna is greatly reduced.
KEY FEATURES

Electrically reconfigurable in terms of gain pattern

Stealth

Frequency hopping

Reduced co-site interferences

Suitable for frequency reflective surfaces
capabilities
We carry out research and development activities
through a extensive combined numerical-experimental investigations



TIMELINE
FUNDED PROJECTS
Researches on plasma antennas started in 2012 exploiting competences matured in the development of plasma thrusters.
2015
Feasibility study and analysis on steering capabilities of smart plasma antennas.
2015
Development of a plasma transmit array for GNSS.
2018
Development of a plasma dipole demonstrator.
2024
Development of a plasma discharge for telecommunications, with new manufacturing techniques like Additive Manufacturing.
2025
Development of a new plasma antenna demonstrator for beam steering in C or X-band.
